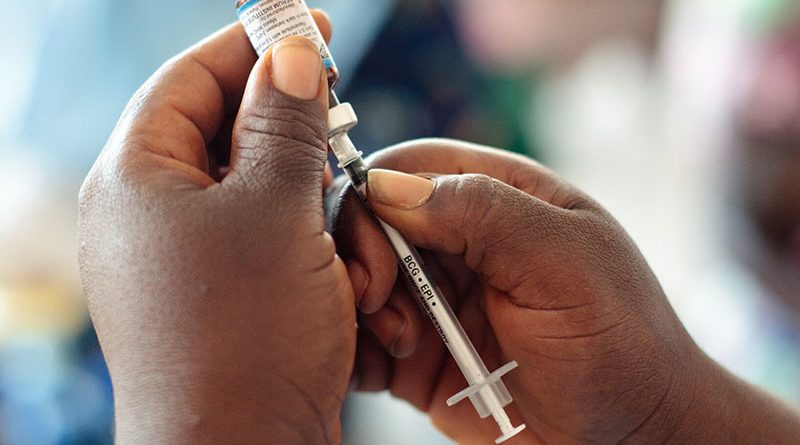
BARRY CHRISTIANSON
FOR the month of July, the rural village of Mbotyi in the Ingquza Hill Municipality in the Eastern Cape has been home to the non-profit Right to Care’s (RTC) rural vaccination team. The team of about 35 consists of drivers, nurses, project managers, data capturers, IT specialists, pharmacists and an emergency medicine specialist.
After helping the Eastern Cape Department of Health with vaccinations during the Sisonke Study period, RTC has focused its efforts on vaccinating the deep rural areas of the Eastern Cape. Wendy Ovens, who is running the pilot project, chose the Ingquza Hill Municipality as its location.
“I know a lot of the population is along the coast. I also know that this area really struggles with access to healthcare services. It’s an area that’s incredibly vulnerable. It’s off the beaten track. It’s not on the N2 … you have to want to come here,” says Ovens, a former urban planner.

Vaccinating in the municipality, which has a mix of high-traffic rural towns and low-density, hard-to-reach rural villages, required a varied approach. In the towns, such as Lusikisiki, they set up vaccination sites at the municipal offices next to the post office on days people were collecting their grants, as well as outside the Boxer supermarket, a high-footfall area. In the more rural areas, such as Makwaleni, Mbotyi or KwaBhumbuta, they set up vaccination sites in schools or community halls.
Things did not always go according to plan. The riots in KwaZulu-Natal in July led to the delay of grant payments, which affected the scheduling of vaccination efforts that were to coincide with those grant payments. RTC was forced to amend their plans.

When vaccinating KwaBhumbuta, the demand was so high, they ran out of vaccines. Sidney Zeeman, the disaster medicine specialist on the team, had to reroute vaccines from two quieter sites in order to not have to send anyone home frustrated.
Other hitches involved transport to and from rural areas. According to Ovens, the team needed to replace 15 tyres in one week. Reflecting on his experience in the rural areas, Zeeman says: “A plan is a basis for change.”

Despite the long days and difficult environment, members of the team remain motivated and are energised by the knowledge of the importance of their role in responding to the pandemic.
“As is apparent in the US, Covid-19 is going to become the disease of the unvaccinated. If we don’t vaccinate in our rural areas, they’re going to become the unvaccinated; they’re going to become the next Covid-19 hotspots. In post-apartheid South Africa, that would be a complete travesty. We can’t let that happen,” says Ovens.
The pilot worked well with RTC vaccinating more than 4 000 people in July. The numbers could have been higher if they were able to vaccinate everyone regardless of age in the towns and the hard-to-reach areas. National guidelines, however, mean they will have to return to the outlying areas they have already visited to vaccinate the age groups they missed in the first round.











The number of confirmed COVID-19 cases in Africa reached 8,024,502 as of Sunday morning, the Africa Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (Africa CDC) said.
The Africa CDC, the specialized healthcare agency of the African Union, said the death toll from the pandemic across the continent stands at 202,915, while some 7,302,535 patients across the continent have recovered from the disease so far.
South Africa, Morocco, Tunisia and Ethiopia are among the countries with the most cases in the continent, according to the agency.
South Africa has recorded the most COVID-19 cases in Africa with 2,854,234 cases, while the northern African country Morocco reported 902,694 cases as of Sunday morning.
In terms of the caseload, southern Africa is the most affected region, followed by the northern and eastern parts of the continent, while central Africa is the least affected region in the continent, according to the Africa CDC.
Addis Ababa, 6th September 2021: African Vaccine Acquisition Trust (AVAT) announces the arrival of 108,000 vaccine doses in Ethiopia as part of the first monthly shipment of Johnson & Johnson vaccines.
AVAT is pleased to announce the shipment of 108,000 vaccine doses of the Johnson & Johnson single-shot vaccines to Ethiopia on 6th September 2021. This is part of a total of 6.4m vaccine doses to be shipped to African Union Member States in August 2021. The Member States who have ordered vaccines through AVAT will continue to receive shipments for the next following months. In collaboration with the Africa Medical Supplies Platform (AMSP), UNICEF is providing logistical and delivery services to the Member States.
These deliveries are part of the historic COVID-19 vaccine advance procurement agreement signed on 28 March 2021 by AVAT for the purchase of 220 million doses of the Johnson & Johnson single-shot COVID-19 vaccine, wit h the potential to order an additional 180 million doses. The agreement and the start of deliveries mark for the first time that the African Union Member States have collectively purchased vaccines to safeguard the health of the African population. In total, the 400m vaccines acquired by AVAT are sufficient to immunise a third of the African population.
The agreement with Johnson & Johnson was made possible through a USD 2 billion facility provided by the African Export-Import Bank (Afreximbank), who are also the Financial and Transaction Advisers, Guarantors, Instalment Payment Advisers and Payment Agents. The United Nations Economic Commission for Africa (UNECA) provided technical support on the financing arrangements and on the alignment of the AU Ministers of Finance.
The Minister of Health of the Federal Democratic Republic of Ethiopia Lia Tadesse, welcomed the arrival of the vaccines and said, “The purchase of these vaccines, will boost our national COVID-19 vaccination programme- in addition to supporting the ongoing rollout of the COVID”
AVAT was established by the African COVID-19 Vaccine Acquisition Task Team, set up in November 2020 under the African Union chairmanship of HE President Cyril Ramaphosa, President of the Republic of South Africa, as part of the African Union’s COVID-19 Vaccine Development and Access Strategy, and its goal of vaccinating at least 60 percent of the African population with safe and efficacious vaccines against COVID-19.
This vaccine acquisition and deployment is also supported by an innovative partnership between the World Bank and the AU, African Vaccine Acquisition Task Team to expedite access to vaccines throughout the continent.
ENDS
About AVAT
The African Vaccine Acquisition Trust (AVAT) is a special purpose vehicle, incorporated in Mauritius. AVAT acts as a centralised purchasing agent on behalf of the African Union (AU) Member States, to secure the necessary vaccines and blended financing resources for achieving Africa’s COVID-19 vaccination strategy which targets vaccinating a minimum of 60% of Africa’s population based on a whole-of-Africa approach. AVAT was established by the COVID-19 African Vaccine Acquisition Task Team, which was set up in November 2020 by President Cyril Ramaphosa, President of the Republic of South Africa, in his capacity as Chairperson of the African Union (AU), as a support component to the COVID-19 Immunisation Strategy that was endorsed by the AU Bureau of Heads of State and Government in August 2020. AVAT’s main partner institutions are the African Union’s Africa Centres for Disease Control and Prevention (Africa CDC), the African Export-Import Bank (Afreximbank) and the United Nations Economic Commission for Africa (ECA).
About Africa CDC
Africa CDC is a specialized technical institution of the African Union that strengthens the capacity and capability of Africa’s public health institutions as well as partnerships to detect and respond quickly and effectively to disease threats and outbreaks, based on data-driven interventions and programmes. Learn more at: www.africacdc.org
About Afreximbank
The African Export-Import Bank (Afreximbank) is a Pan-African multilateral financial institution with the mandate of financing and promoting intra-and extra-African trade. Afreximbank was established in October 1993 and owned by African governments, the African Development Bank and other African multilateral financial institutions as well as African and non-African public and private investors. The Bank was established under two constitutive documents, an Agreement signed by member states, which confers on the Bank the status of an international organization, and a Charter signed by all Shareholders, which governs its corporate structure and operations. Afreximbank deploys innovative structures to deliver financing solutions that are supporting the transformation of the structure of Africa’s trade, accelerating industrialization and intra-regional trade, thereby sustaining economic expansion in Africa. At the end of 2020, the Bank’s total assets and guarantees stood at US$21.5 billion and its shareholders’ funds amounted to US$3.4 billion. The Bank disbursed more than US$42 billion between 2016 and 2020. Afreximbank has ratings assigned by GCR (international scale) (A-), Moody’s (Baa1) and Fitch (BBB-). The Bank is headquartered in Cairo, Egypt. For more information, visit: www.afreximbank.com Follow us on Twitter | Facebook | LinkedIn | Instagram
About ECA
Established by the Economic and Social Council (ECOSOC) of the United Nations (UN) in 1958 as one of the UN’s five regional commissions, the United Nations Economic Commission for Africa’s (ECA’s) mandate is to promote the economic and social development of its Member States, foster intraregional integration and promote international cooperation for Africa’s development. ECA is made up of 54 Member States and plays a dual role as a regional arm of the UN and as a key component of the African institutional landscape. For more information, visit: www.uneca.org
About AMSP
The Africa Medical Supplies Platform (AMSP) is a non-profit initiative launched by the African Union as an immediate, integrated and practical response to the Covid-19 pandemic. The online platform was developed under the leadership of the African Union Special Envoy, Strive Masiyiwa and powered by Janngo on behalf of the African Union’s Africa Centres for Disease Control and Prevention (Africa CDC) and in partnership with African Export-Import Bank (Afreximbank) and United Nations Economic Commission for Africa (ECA) with the support of leading African & international Institutions, Foundations & Corporations as well as Governments of China, Canada & France. For more information visit www.amsp.africa
About The World Bank
Since the start of the COVID-19 pandemic, the World Bank Group has deployed over $157 billion to fight the health, economic, and social impacts of the pandemic, the fastest and largest crisis response in its history. The financing is helping more than 100 countries strengthen pandemic preparedness, protect the poor and jobs, and jump start a climate-friendly recovery. The Bank is also supporting over 50 low- and middle-income countries, more than half of which are in Africa, with the purchase and deployment of COVID-19 vaccines, and is making available $20 billion in financing for this purpose until the end of 2022.
About UNICEF
UNICEF works in some of the world’s toughest places, to reach the world’s most disadvantaged children. Across more than 190 countries and territories, we work for every child, everywhere, to build a better world for everyone. Follow UNICEF on Twitter, Facebook, Instagram and YouTube
MEDIA CONTACTS
AVAT: George Sibotshiwe – This email address is being protected from spambots. You need JavaScript enabled to view it. / +27 71 467 7689
AFRICA CDC: Dr Nicaise Ndembi – This email address is being protected from spambots. You need JavaScript enabled to view it.
AFREXIMBANK: Amadou Labba Sall – This email address is being protected from spambots. You need JavaScript enabled to view it.
UNECA: Nita Deerpalsing – This email address is being protected from spambots. You need JavaScript enabled to view it.
AMSP: Antonia Gleizes – This email address is being protected from spambots. You need JavaScript enabled to view it.
WORLD BANK: Moses Alex Kargbo – This email address is being protected from spambots. You need JavaScript enabled to view it. UNICEF: Tapuwa Mutseyekwa – This email address is being protected from spambots. You need JavaScript enabled to view it..
Brazzaville, 2 September 2021 – Africa is set to miss the urgent global goal of vaccinating the most vulnerable 10% of every country’s population against COVID-19 by the end of September. Forty-two of Africa’s 54 nations—nearly 80%—are set to miss the target if the current pace of vaccine deliveries and vaccinations hold, new data from the World Health Organization (WHO) shows.
Nine African countries, including South Africa, Morocco and Tunisia, have already reached the global target set in May by the World Health Assembly, the world’s highest health policy-setting body. At the current pace, three more African countries are set to meet the target. Two more could meet it if they speed up vaccinations.
“With less than a month to go, this looming goal must concentrate minds in Africa and globally. Vaccine hoarding has held Africa back and we urgently need more vaccines, but as more doses arrive, African countries must zero in and drive forward precise plans to rapidly vaccinate the millions of people that still face a grave threat from COVID-19,” said Dr Matshidiso Moeti, WHO Regional Director for Africa.
Almost 21 million COVID-19 vaccines arrived in Africa via the COVAX Facility in August, an amount equal to the previous four months combined. With more vaccines expected from COVAX and the African Union by the end of September, we could see enough doses delivered to meet the 10% target.
While many African countries have sped up COVID-19 vaccinations as vaccine shipments ramped up in August, 26 countries have used less than half of their COVID-19 vaccines.
Over 143 million doses have been received in Africa in total and 39 million people—around just 3% of Africa’s population—are fully vaccinated. In comparison, 52% of people are fully vaccinated in the United States of America and 57% in the European Union.
“The inequity is deeply disturbing. Just 2% of the over five billion doses given globally have been administered in Africa. Yet recent rises in vaccine shipments and commitments shows that a fairer, more just global distribution of vaccines looks possible,” said Dr Moeti.
Countries must continue to address operational gaps and continually improve, adapt and refine their COVID-19 vaccination campaigns. Of the 30 countries that have submitted data to WHO on operational readiness, one in two have not conducted intra-action reviews, which are key to assessing and fine-tuning progress. One in three countries have not updated their National Vaccine Deployment Plans, which instruct all COVID-19 vaccination actions in each country.
WHO is providing tailored policy advice and technical guidance and support to African countries to help enhance their logistics, planning and monitoring capacities. WHO is also working to share valuable lessons and experiences between countries.
COVID-19 cases are declining slightly in Africa but remain stubbornly high. A rising number of new cases in Central, East and West Africa pushed case numbers up to nearly 215 000 in the week ending on 29 August. Twenty-five countries—over 45% of African countries—are reporting high or fast-rising case numbers. Over 5500 deaths were reported in the week ending on 29 August.
“Although Africa’s third wave peaked in July, the decline in new cases is at a glacial pace—far slower than in previous waves. The pandemic is still raging in Africa and we must not let our guard down. Every hour 26 Africans die of COVID-19.”
The highly transmissible Delta variant has been found in 31 African countries. The Alpha variant has been detected in 44 countries and the Beta variant in 39.
The C.1.2 variant has been identified in 114 cases in South Africa. Single cases have been found in four other African countries, and very low case numbers have been reported internationally. While first reported to WHO in July, the prevalence of this new variant remains very low. To be identified as a variant of concern there must be evidence of an impact on transmissibility, severity or immunity. This is not the case for the C.1.2 variant, yet more data is required.
“We are closely monitoring the spread and evolution of all reported variants of COVID-19, including C.1.2. Mask wearing, physical distancing and regular hand washing will help keep you safe from all variants,” said Dr Moeti.
Dr Moeti spoke during a virtual press conference today facilitated by APO Group. She was joined by Dr Nicholas Crisp, Deputy Director General, National Health Insurance, Department of Health, South Africa, and Dr Assan Abdoul Nasser, Director of Immunizations, Ministry of Public Health, Population and Social Affairs, Niger.
Also on hand to respond to questions were Dr Richard Mihigo, Coordinator, Immunization and Vaccines Development Programme, WHO Regional Office for Africa, and Dr Thierno Balde, Regional COVID-19 Deputy Incident Manager, WHO Regional Office for Africa.
(END)
For Additional Information or to Request Interviews, Please Contact:
Collins Boakye-Agyemang
Communications and Marketing Officer
Tel: + 242 06 520 65 65 (WhatsApp)
Email: This email address is being protected from spambots. You need JavaScript enabled to view it.
Saya Oka
Communications Officer, WHO Africa Health Emergencies Programme
Tel: +242 06 508 1009
Email: This email address is being protected from spambots. You need JavaScript enabled to view it.